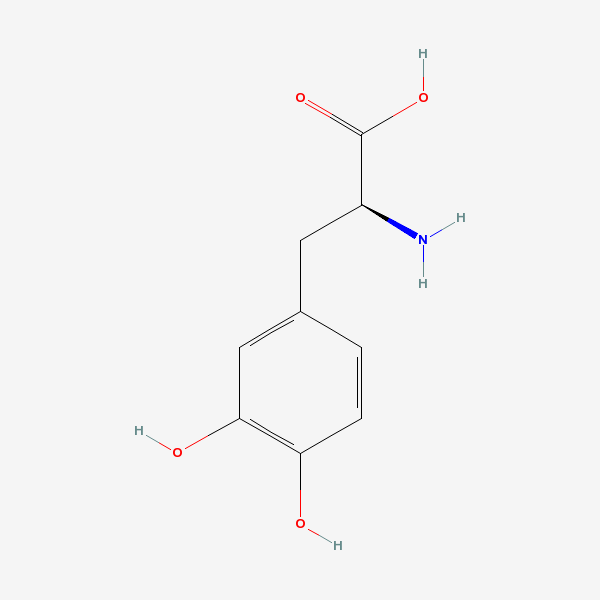
L-dopa
 L-dopa - definition from Biology-Online.org
L-dopa - definition from Biology-Online.org
[levodopa (Science: chemical) The naturally occurring form of dopa and the immediate precursor of dopamine. unlike dopamine itself, it can be taken orally and crosses the blood-brain barrier. It is rapidly taken up by dopaminergic neurons and converted to dopamine. It is used for the treatment of parkinsonism and is usually given with agents that inhibit its conversion to dopamine outside of the [[central nervous system
InChI: InChI=1/C9H11NO4/c10-6(9(13)14)3-5-1-2-7(11)8(12)4-5/h1-2,4,6,11-12H,3,10H2,(H,13,14)/t6-/m0/s1
InChIKey: InChIKey=WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIEBA
SMILES: N[C@@H](CC1=CC(O)=C(O)C=C1)C(O)=O
CAS number 59-92-7
Names:
Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
Levodopa
L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine
L-Dopa
L-dopa
L-Dopa
L-DOPA
L-dopa
3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE
3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
3,4-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
3-Hydroxy-L-tyrosine
Registries:
PubChem CID 6047
Beilstein =2215169
CAS 59-92-7 (from NIST)
ChEBI 15765
chemPDB DAH
COMe MOL000169
Kegg C00355
PubChem ID 3648
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|