Ingredients --
Caffeine
Chemical Formula:
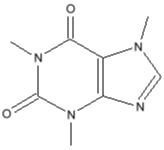
Synonyms
TrimethylxanthineDescription
White crystaline powder with a bitter taste.Uses
Caffeine is an addictive drug used in soft drinks as a stimulant. It occurs naturally in coffee, tea, and chocolate. It is added to pain relievers because it enhances the effects of aspirin and because many headaches are caused by caffeine withdrawal. Caffeine closes down blood vessels by competing with adenosine, and helps alleviate the vascular headaches caused by withdrawal. A cup of drip-brewed coffee typically contains 100 milligrams of caffeine per 177 milliliters (6 ounces). Tea has about 70 milligrams, and colas have about 50 milligrams. A bar of milk chocolate has about 36 milligrams in 177 milliliters. Caffeine binds to adenosine receptors in the brain, preventing adenosine from inducing sleep, or opening blood vessels. Caffeine also increases levels of dopamine, the neurotransmitter associated with pleasure (this is the mechanism for addiction). The response to adenosine competition causes increased adrenaline flow.caffeine: InChI=1/C8H10N4O2/c1-10-4-9-6-5(10)7(13)12(3)8(14)11(6)2/h4H,1-3H3
By Simon Quellen Field