Ingredients --
Benzocaine
Chemical Formula:
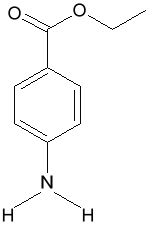
Benzocaine
Synonyms
Ethyl p-aminobenzoateEthyl PABA
Anesthesin
Description
White crystalline powder.Uses
Benzocaine is a topical anesthetic. It numbs wherever it is applied. It is widely used in first aid creams and sunburn remedies.Chemistry lesson
Benzocaine is an ester, a compound made from the organic acid PABA (para amino benzoic acid) and the alcohol ethanol.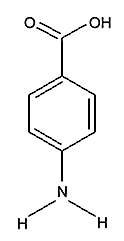
Para amino benzoic acid Other esters of PABA have similar anesthetic properties.
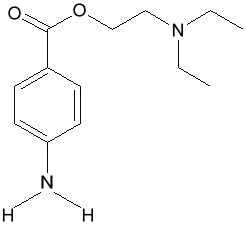
Procaine (novocaine) Dentists use procaine (also called novocaine) to numb teeth and gums before dental work.
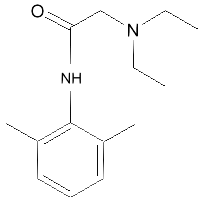
Lidocaine (xylocaine) Another topical anesthetic, similar to benzocaine, is lidocaine, which is used to relive the pain of shingles (herpes zoster) infections. Lidocaine is called an amide anesthetic, because it is not an ester (the alcohol is replaced by an amide, the nitrogen group). Amide anesthetics are metabolized by the liver, and are less prone to cause allergic reactions. If an anesthetic has an "i" in the prefix (lidocaine, prilocaine, bupivicaine) it is an amide anesthetic.
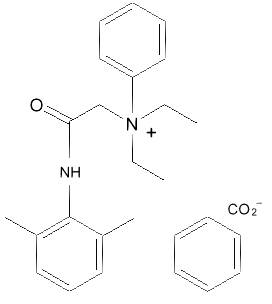
Denatonium benzoate A small change to lidocaine (adding a benzyl group) makes the molecule denatonium benzoate, the bitterest tasting substance known. It is used to denature alcohol, (Specially Denatured alcohol 40, or SD-40, is ethanol denatured (made unfit for drinking) by a tiny amount denatonium benzoate).
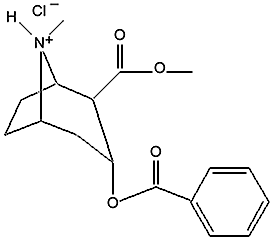
Cocaine hydrochloride You can see a resemblance between benzocaine, procaine, and the compound that gave Coca Cola its first name. Cocaine also has a numbing effect, in addition to its effects as an addictive central nervous system stimulant. Some other anesthetics with similar structures are prilocaine, tetracaine, ropivacaine, bupivacaine, chloroprocaine, and mepivacaine:
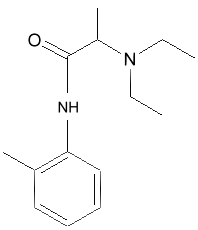
Prilocaine
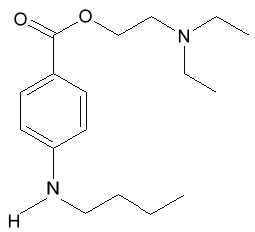
Tetracaine
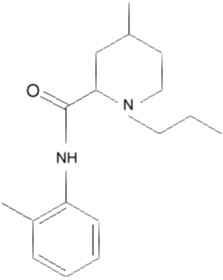
Ropivacaine
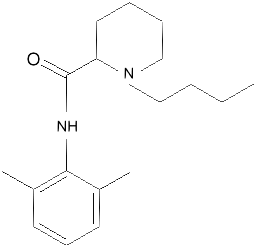
Bupivicaine
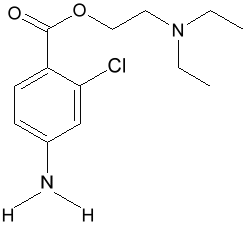
Chloroprocaine
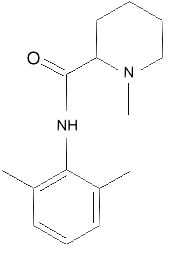
Mepivacaine
denatonium benzoate: InChI=1/C21H28N2O.C7H6O2/c1-5-23(6-2,15-19-13-8-7-9-14-19)16-20(24)22-21-17(3)11-10-12-18(21)4;8-7(9)6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h7-14H,5-6,15-16H2,1-4H3;1-5H,(H,8,9)/fC21H29N2O.C7H5O2/h22H;/q+1;-1
cocaine hydrochloride: InChI=1/C17H21NO4.ClH/c1-18-12-8-9-13(18)15(17(20)21-2)14(10-12)22-16(19)11-6-4-3-5-7-11;/h3-7,12-15H,8-10H2,1-2H3;1H/t12-,13+,14-,15+;/m0./s1
cocaine hydrochloride: InChI=1/C17H21NO4.ClH/c1-18-12-8-9-13(18)15(17(20)21-2)14(10-12)22-16(19)11-6-4-3-5-7-11;/h3-7,12-15H,8-10H2,1-2H3;1H
cocaine hydrochloride: InChI=1/C17H21NO4.ClH/c1-18-12-8-9-13(18)15(17(20)21-2)14(10-12)22-16(19)11-6-4-3-5-7-11;/h3-7,12-15H,8-10H2,1-2H3;1H/t12-,13-,14+,15-;/m1./s1
cocaine hydrochloride: InChI=1/C17H21NO4.ClH/c1-18-12-8-9-13(18)15(17(20)21-2)14(10-12)22-16(19)11-6-4-3-5-7-11;/h3-7,12-15H,8-10H2,1-2H3;1H/t12-,13-,14+,15-;/m1./s1
benzocaine: InChI=1/C9H11NO2/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6H,2,10H2,1H3
chloroprocaine: InChI=1/C13H19ClN2O2/c1-3-16(4-2)7-8-18-13(17)11-6-5-10(15)9-12(11)14/h5-6,9H,3-4,7-8,15H2,1-2H3
haloperidol: InChI=1/C21H23ClFNO2/c22-18-7-5-17(6-8-18)21(26)11-14-24(15-12-21)13-1-2-20(25)16-3-9-19(23)10-4-16/h3-10,26H,1-2,11-15H2
mepivacaine: InChI=1/C15H22N2O/c1-11-7-6-8-12(2)14(11)16-15(18)13-9-4-5-10-17(13)3/h6-8,13H,4-5,9-10H2,1-3H3,(H,16,18)/f/h16H
prilocaine: InChI=1/C13H20N2O/c1-4-9-14-11(3)13(16)15-12-8-6-5-7-10(12)2/h5-8,11,14H,4,9H2,1-3H3,(H,15,16)/f/h15H
procaine: InChI=1/C13H20N2O2/c1-3-15(4-2)9-10-17-13(16)11-5-7-12(14)8-6-11/h5-8H,3-4,9-10,14H2,1-2H3
ropivacaine: InChI=1/C17H26N2O/c1-4-11-19-12-6-5-10-15(19)17(20)18-16-13(2)8-7-9-14(16)3/h7-9,15H,4-6,10-12H2,1-3H3,(H,18,20)/t15-/m0/s1/f/h18H
tetracaine: InChI=1/C15H24N2O2/c1-4-5-10-16-14-8-6-13(7-9-14)15(18)19-12-11-17(2)3/h6-9,16H,4-5,10-12H2,1-3H3
By Simon Quellen Field