Ingredients --
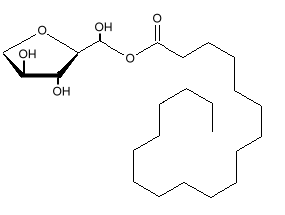
Sorbitan monostearate
Chemical Formula:
Sorbitan monostearate
Synonyms
SPAN 60Description
Wax-like creamy white powder. Sorbitan monostearate is an ester of sorbitol and stearic acid. The sorbitol end of the molecule is very soluble in water. The stearic acid end is soluble in fats. These properties make the molecule very good at making emulsions of oil and water. It is sometimes known as a synthetic wax.Uses
Sorbitan monostearate is used as an emulsifying agent in cake mixes, icings, baked goods, puddings, imitation whipped cream, hemorrhoid creams, and creams to treat dry skin. It is often used with polysorbate 80. Similar molecules can be made using other fatty acids, such as the shorter chained lauric acid.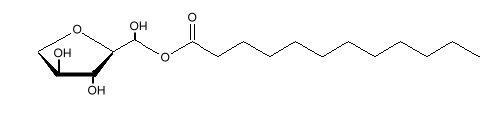
Sorbitan monolaurate