Ingredients --
Saffron
Chemical Formula:

β-gentobiose crocetin
Synonyms
β-gentobiose crocetin,Saffron carotenoids
Description
Saffron is one of the most expensive spices used today. It is the tiny stigma of the Crocus flower Crocus sativa. Each tiny stigma is plucked from the flower by hand. The dye molecule in saffron is the carotenoid β-gentobiose crocetin. It is related to β-carotene, and you can see the relationship in the center of the molecule. That center portion is the carotenoid pigment crocetin: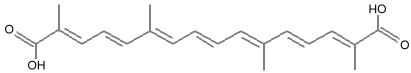
Crocetin On either side of the crocetin molecule is a disaccharide molecule called β-gentobiose, and the result is the molecule that gives saffron its yellow color.
Uses
Saffron is a spice, added sometimes for flavor, but mostly for the yellow color it imparts to foods. Because of its expense, saffron is often replaced in recipes by another carotenoid, annatto or the unrelated dye molecule in turmeric. Like the other carotenoid dyes, saffron is an anti-oxidant, but its expense makes it unsuitable as a preservative or dietary supplement.crocetin: InChI=1/C20H24O4/c1-15(11-7-13-17(3)19(21)22)9-5-6-10-16(2)12-8-14-18(4)20(23)24/h5-14H,1-4H3,(H,21,22)(H,23,24)/b6-5+,11-7+,12-8+,15-9+,16-10+,17-13+,18-14+/f/h21,23H
By Simon Quellen Field