Ingredients --
Carmine
Chemical Formula:
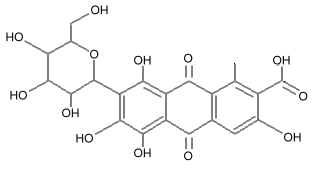
Carminic acid
Synonyms
Cochineal extract,7-D-glucopyranosyl-3,5,6,8-tetrahydroxy-1-methyl-9.10-dioxoanthracene-2-carboxylic acid
Description
Carmine is a colored pigment extracted from the female insect Coccus cacti or Dactylopius coccus, or their eggs. The insects live on prickly pear cactus in Mexico. The Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés brought the dye to Europe after seeing the Aztecs use it. Because carmine comes from insects, some other color must be used if a product is to be labeled kosher. It takes over a million of the insects to make a pound of dye. The insects are harvested when the females are about to lay eggs, at which time they turn a bright red color. The shells of the female insects are dried, then the color is dissolved in a solvent, and all of the insect parts are filtered out. Because of all of this labor intensive processing, carmine is more expensive than FD&C Red #40, but it has a deep magenta-red color, and red 40 is more orange-red.Uses
Carmine (or cochineal) is used as a food coloring, in cosmetics, and in paints. Carminic acid is orange in acidic media (pH 3), red in nearly neutral media (pH 5.5) and purple at pH 7. It forms complexes with metals such as tin and aluminum to make brilliant red pigments. Carmine is easily bleached by sulfur dioxide. Carminic acid is related to another dye molecule, alizarin.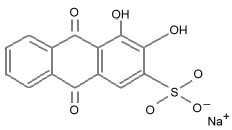
Alizarin 6 Also note the similarity to erythrosin B, known as FD&C red #3:
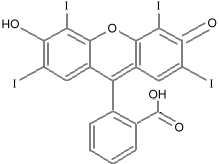
Erythrosin B
carminic acid: InChI=1/C22H20O13/c1-4-8-5(2-6(24)9(4)22(33)34)13(25)10-11(15(8)27)16(28)12(18(30)17(10)29)21-20(32)19(31)14(26)7(3-23)35-21/h2,7,14,19-21,23-24,26,28-32H,3H2,1H3,(H,33,34)/t7-,14-,19+,20-,21-/m1/s1/f/h33H
alizarin: InChI=1/C14H8O4/c15-10-6-5-9-11(14(10)18)13(17)8-4-2-1-3-7(8)12(9)16/h1-6,15,18H
By Simon Quellen Field